


Jun 28, 2023
Jun 28, 2023
Webinar key takeaways | Building an e-commerce growth engine (part I)
Webinar key takeaways | Building an e-commerce growth engine (part I)
Written by
Written by
Aurelija Vyčaitė
Aurelija Vyčaitė
Webinars
In the second webinar of our series, Jons Janssens delves into the execution and data components of the digital commerce operating model, going a step beyond the strategic considerations of the first session.
If you want to watch the recording of the full webinar "Building an e-commerce growth engine", find it here.

Centring on the concept of a growth engine, in this article, will present a framework for achieving sustainable e-commerce growth.
We will share insight into building a successful e-commerce growth engine for long-term success, focusing on customer-centricity, data ownership, and balancing acquisition and retention. In the upcoming second part, we will delve deeper into aligning a cross-functional team and specific growth tactics to maximize the potential of your growth engine.
In the second webinar of our series, Jons Janssens delves into the execution and data components of the digital commerce operating model, going a step beyond the strategic considerations of the first session.
If you want to watch the recording of the full webinar "Building an e-commerce growth engine", find it here.

Centring on the concept of a growth engine, in this article, will present a framework for achieving sustainable e-commerce growth.
We will share insight into building a successful e-commerce growth engine for long-term success, focusing on customer-centricity, data ownership, and balancing acquisition and retention. In the upcoming second part, we will delve deeper into aligning a cross-functional team and specific growth tactics to maximize the potential of your growth engine.
Understanding the Growth Engine: Why Should You Care About It?
Understanding the Growth Engine: Why Should You Care About It?
In the simplest explanation, the main idea of the growth engine is that if you treat your customers right, they will tell their friends about you. In turn, they will be tempted to try your product or service. This way, you focus less on advertising and more on customer centricity, making your growth more predictable, profitable, and long-term oriented.
Numerous studies have proven that no kind of advertising beats the power of a satisfied customer’s word: almost 90% of Nielsen study respondents claimed they trust recommendations from people they know. Ephemeral marketing activities, such as television campaigns and paid online ads, are not only less trusted but also rarely bring sustained, continued growth.
In the simplest explanation, the main idea of the growth engine is that if you treat your customers right, they will tell their friends about you. In turn, they will be tempted to try your product or service. This way, you focus less on advertising and more on customer centricity, making your growth more predictable, profitable, and long-term oriented.
Numerous studies have proven that no kind of advertising beats the power of a satisfied customer’s word: almost 90% of Nielsen study respondents claimed they trust recommendations from people they know. Ephemeral marketing activities, such as television campaigns and paid online ads, are not only less trusted but also rarely bring sustained, continued growth.
In the simplest explanation, the main idea of the growth engine is that if you treat your customers right, they will tell their friends about you. In turn, they will be tempted to try your product or service. This way, you focus less on advertising and more on customer centricity, making your growth more predictable, profitable, and long-term oriented.
Numerous studies have proven that no kind of advertising beats the power of a satisfied customer’s word: almost 90% of Nielsen study respondents claimed they trust recommendations from people they know. Ephemeral marketing activities, such as television campaigns and paid online ads, are not only less trusted but also rarely bring sustained, continued growth.
In the simplest explanation, the main idea of the growth engine is that if you treat your customers right, they will tell their friends about you. In turn, they will be tempted to try your product or service. This way, you focus less on advertising and more on customer centricity, making your growth more predictable, profitable, and long-term oriented.
Numerous studies have proven that no kind of advertising beats the power of a satisfied customer’s word: almost 90% of Nielsen study respondents claimed they trust recommendations from people they know. Ephemeral marketing activities, such as television campaigns and paid online ads, are not only less trusted but also rarely bring sustained, continued growth.
LTV:CAC ratio
LTV:CAC ratio
In contrast, the idea of a growth engine is to tie all efforts directly to commercial success metrics. We call it the LTV: CAC ratio, which explains whether the cost to acquire a new customer (CAC) is lower than the net profit the customer brought to the company throughout the entire relationship (LTV). A good benchmark for success? Aim for the LTV: CAC ratio = 3:1, meaning, on average, each customer brings three times more net profit than the acquisition costs needed to initiate the relationship with them. As your customer base increases, the average LTV also tends to increase, creating a snowball effect and making your growth engine more profitable. The graph below is an example visualisation, provided by Corporate Finance Institute.
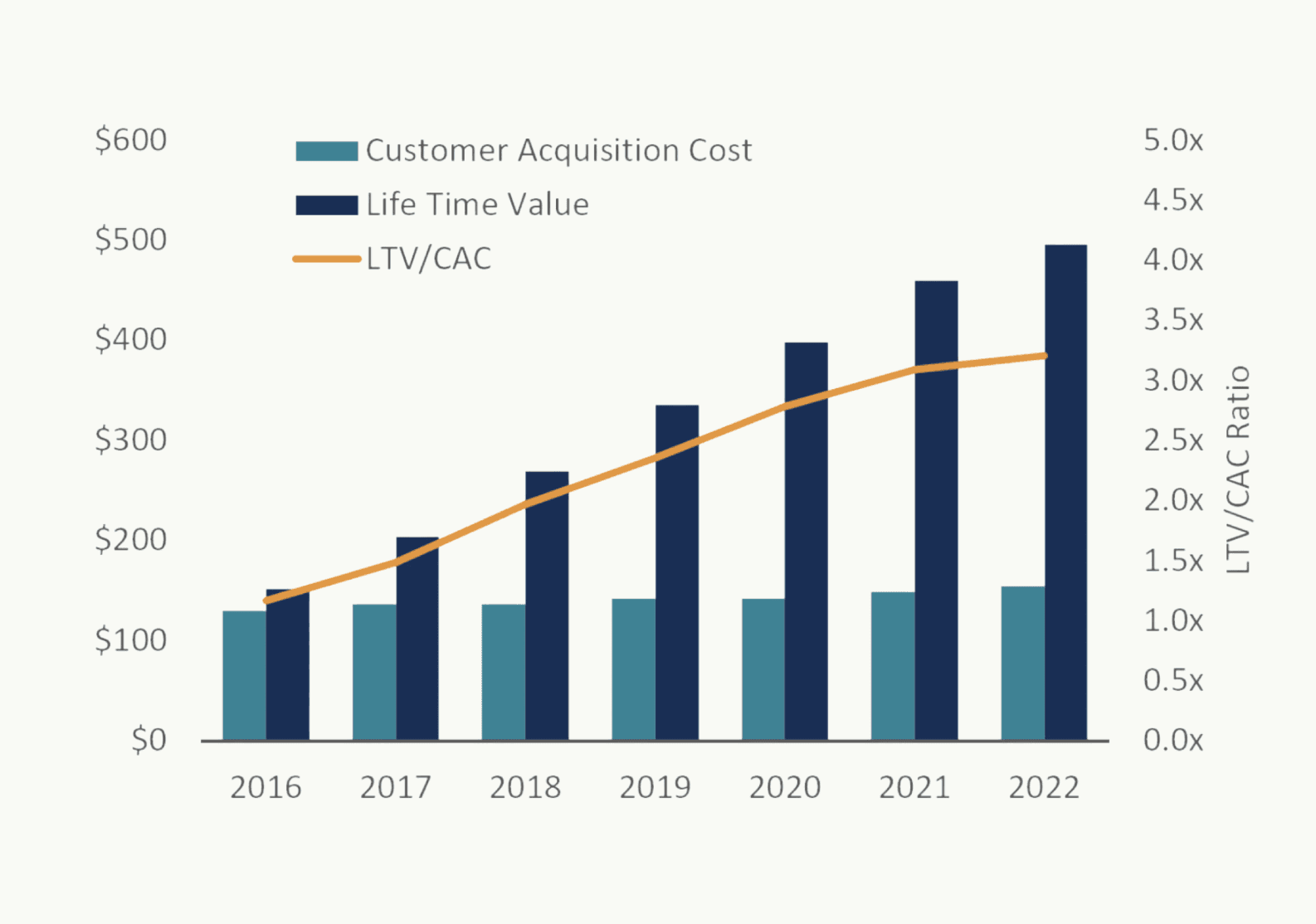
This rather simple math explains why referrals, positive reviews, or retention, in general, are so crucial for the growth engine’s success. However, bear in mind: the growth engine, unlike paid advertising awareness, cannot be bought. It can only be earned through systemic processes, strong team alignment, and continuous focus on customer needs. And it takes time.
In contrast, the idea of a growth engine is to tie all efforts directly to commercial success metrics. We call it the LTV: CAC ratio, which explains whether the cost to acquire a new customer (CAC) is lower than the net profit the customer brought to the company throughout the entire relationship (LTV). A good benchmark for success? Aim for the LTV: CAC ratio = 3:1, meaning, on average, each customer brings three times more net profit than the acquisition costs needed to initiate the relationship with them. As your customer base increases, the average LTV also tends to increase, creating a snowball effect and making your growth engine more profitable. The graph below is an example visualisation, provided by Corporate Finance Institute.

This rather simple math explains why referrals, positive reviews, or retention, in general, are so crucial for the growth engine’s success. However, bear in mind: the growth engine, unlike paid advertising awareness, cannot be bought. It can only be earned through systemic processes, strong team alignment, and continuous focus on customer needs. And it takes time.

Principle 1: Ownership of customer data
Principle 1: Ownership of customer data
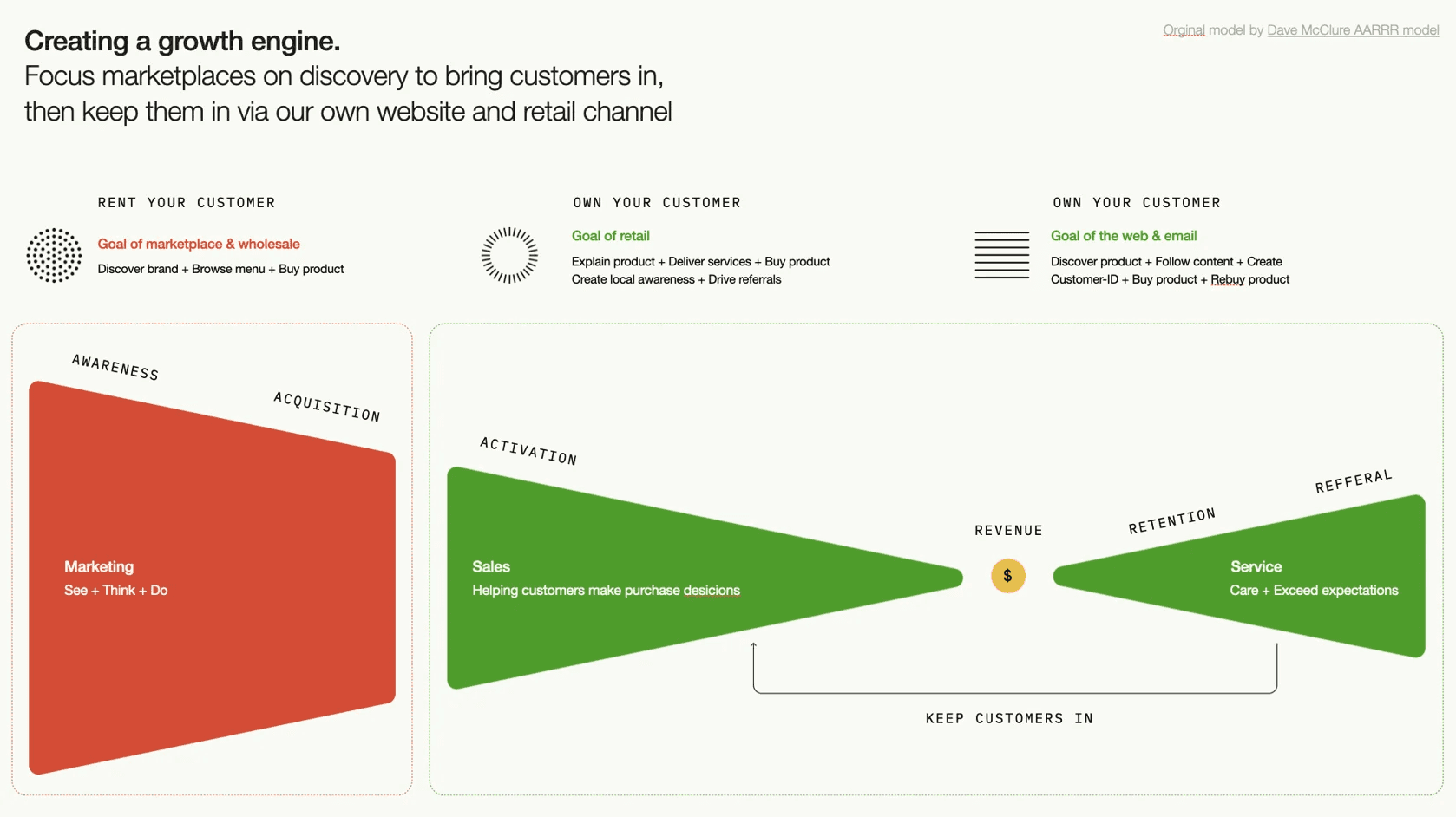
In the current marketplace landscape, it's paramount to understand the origin of your customer data. Selling via marketplaces like Amazon can relinquish control over customer relationships. In contrast, direct channels such as retail or the web allow businesses to own customer data, offering the advantage of implementing retention strategies.
Owning customer data is fundamental for a successful growth engine. While marketplaces can help penetrate new markets, the ultimate goal should be to encourage customer loyalty on your own channels. Essentially, marketplaces should be used for customer discovery and then, retention should be driven through your own website and retail channel.
In the current marketplace landscape, it's paramount to understand the origin of your customer data. Selling via marketplaces like Amazon can relinquish control over customer relationships. In contrast, direct channels such as retail or the web allow businesses to own customer data, offering the advantage of implementing retention strategies.
Owning customer data is fundamental for a successful growth engine. While marketplaces can help penetrate new markets, the ultimate goal should be to encourage customer loyalty on your own channels. Essentially, marketplaces should be used for customer discovery and then, retention should be driven through your own website and retail channel.
Acquisition Funnel: from awareness to conversion
Acquisition Funnel: from awareness to conversion
While retention is crucial to the growth engine, there’s no point expecting something from it if there is little to no traffic to your sales channels. So, how to drive it the right way?
Here we present the acquisition funnel, which is designed to consistently and predictably attract new customers. It aims to avoid “leakages”: customers dropping off at various stages before reaching the point of conversion. However, keep in mind that it is not a magic and universal formula to generate massive demand in a short time. Instead, it’s a tried and tested process that, if implemented with genuine care, will orchestrate and focus the customer acquisition efforts.
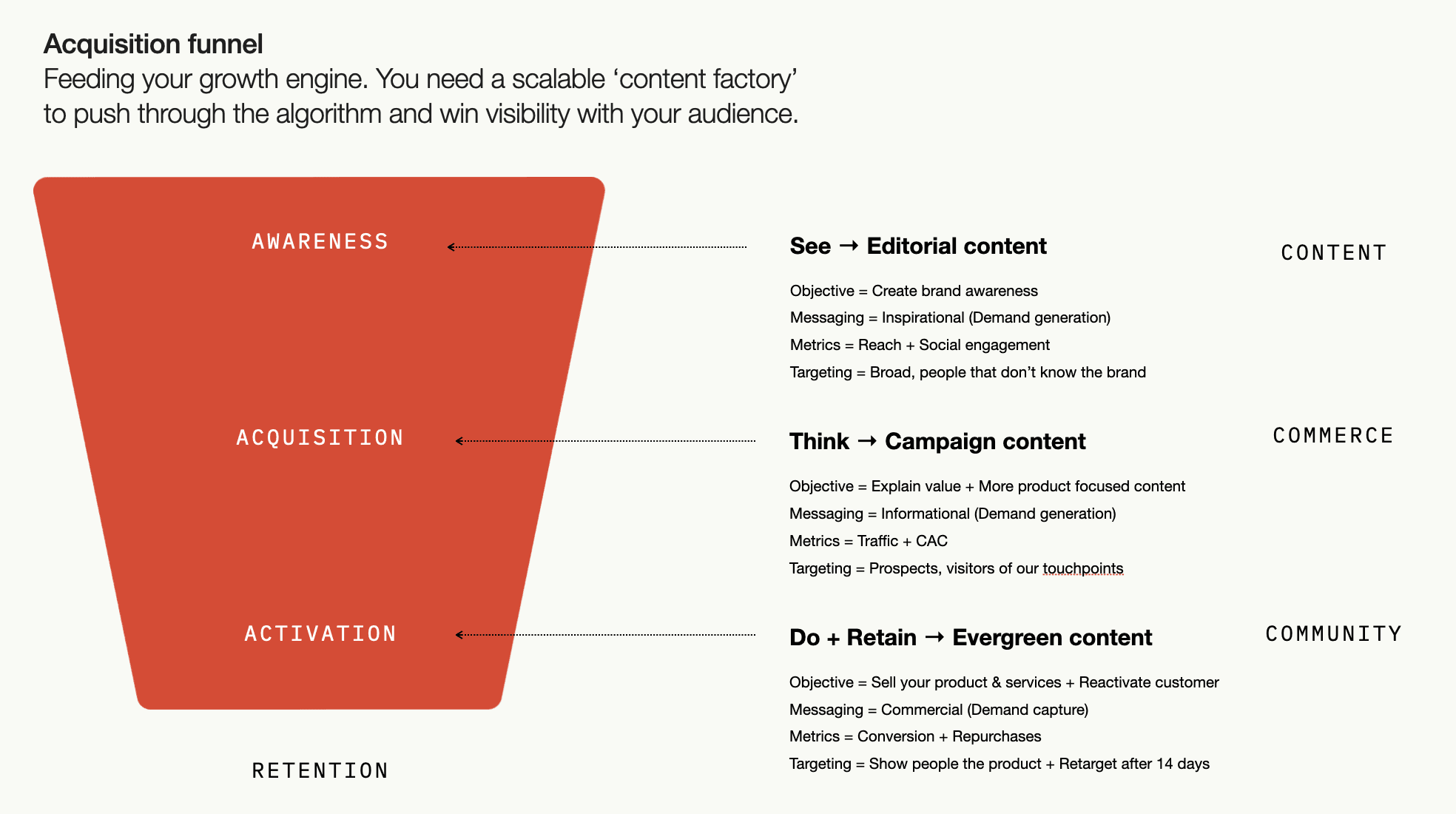
As you can see in the figure above, the acquisition funnel is divided into three parts: awareness, acquisition, and activation with See → Think → Do counterparts, respectively.
While the awareness stage is about creating brand awareness through inspirational messaging, the acquisition stage is more about practical and product-focused content that helps in making the purchase decision. The activation stage is the most commercially oriented, with more “hard” conversion messaging.
Feeding this acquisition funnel and, by extension, the growth engine requires a significant amount of content, so much so that it's often likened to operating a Content Factory. This demand for content arises from the need to push through the algorithms of various social media feeds, making the brand's presence known and felt. Thus, combining content and paid media becomes the key to achieving visibility with your audience.
While retention is crucial to the growth engine, there’s no point expecting something from it if there is little to no traffic to your sales channels. So, how to drive it the right way?
Here we present the acquisition funnel, which is designed to consistently and predictably attract new customers. It aims to avoid “leakages”: customers dropping off at various stages before reaching the point of conversion. However, keep in mind that it is not a magic and universal formula to generate massive demand in a short time. Instead, it’s a tried and tested process that, if implemented with genuine care, will orchestrate and focus the customer acquisition efforts.

As you can see in the figure above, the acquisition funnel is divided into three parts: awareness, acquisition, and activation with See → Think → Do counterparts, respectively.
While the awareness stage is about creating brand awareness through inspirational messaging, the acquisition stage is more about practical and product-focused content that helps in making the purchase decision. The activation stage is the most commercially oriented, with more “hard” conversion messaging.
Feeding this acquisition funnel and, by extension, the growth engine requires a significant amount of content, so much so that it's often likened to operating a Content Factory. This demand for content arises from the need to push through the algorithms of various social media feeds, making the brand's presence known and felt. Thus, combining content and paid media becomes the key to achieving visibility with your audience.
Metrics Model: Balancing Acquisition and Retention
Metrics Model: Balancing Acquisition and Retention
Performance measurement of the growth engine requires a robust metrics model. Acquisition of new customers is generally more expensive than reactivating existing ones, making it crucial to balance acquisition and retention. This balance guides decision-making on time and budget allocation.
The LTV to CAC ratio is the crux of long-term growth. If this ratio is above three, it indicates a healthy growth engine. But how to get to that?
The metrics model of the growth engine focuses on customer centricity: turning strangers into your brand promoters. Essentially there are three areas where performance matters most in achieving that: marketing, sales, and service. Measure these metrics and their performance will guide you in identifying challenges, opportunities, and will guide your efforts.
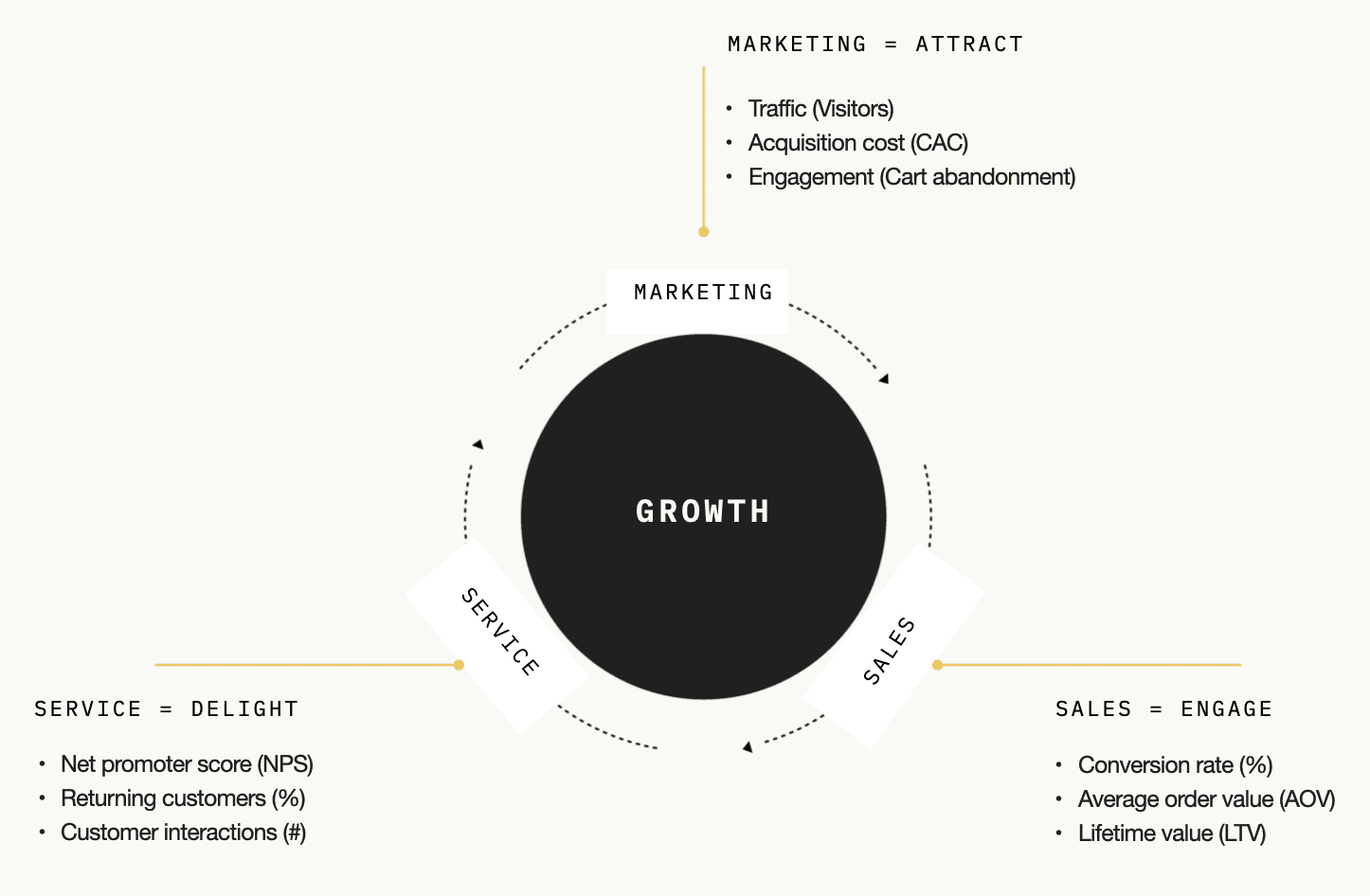
Performance measurement of the growth engine requires a robust metrics model. Acquisition of new customers is generally more expensive than reactivating existing ones, making it crucial to balance acquisition and retention. This balance guides decision-making on time and budget allocation.
The LTV to CAC ratio is the crux of long-term growth. If this ratio is above three, it indicates a healthy growth engine. But how to get to that?
The metrics model of the growth engine focuses on customer centricity: turning strangers into your brand promoters. Essentially there are three areas where performance matters most in achieving that: marketing, sales, and service. Measure these metrics and their performance will guide you in identifying challenges, opportunities, and will guide your efforts.

Principle 3: CAC is the new rent
Principle 3: CAC is the new rent
One may compare CAC to the commercial space rent in physical retail. A brick-and-mortar store pays rent to get a better location for its store space to attract foot traffic. Meanwhile, online shops won’t bring many passersby; they will fight for lower CAC and an efficient acquisition funnel to attract online traffic. CAC is the essential cost for an online shop, just like rent in physical retail. Although low CAC is often the goal, just like a brick-and-mortar store, you may pay higher rent to attract higher-value customers to improve your LTV metric. In other words, it’s about the balance: higher LTV can potentially mean higher CAC too.
One may compare CAC to the commercial space rent in physical retail. A brick-and-mortar store pays rent to get a better location for its store space to attract foot traffic. Meanwhile, online shops won’t bring many passersby; they will fight for lower CAC and an efficient acquisition funnel to attract online traffic. CAC is the essential cost for an online shop, just like rent in physical retail. Although low CAC is often the goal, just like a brick-and-mortar store, you may pay higher rent to attract higher-value customers to improve your LTV metric. In other words, it’s about the balance: higher LTV can potentially mean higher CAC too.
Stay tuned for part II
We hope these principles have shed some light on how a growth engine can drive long-term success for your e-commerce business. However, this is only part one. In the second part of this series, we'll delve into how to align a cross-functional team to contribute to developing your growth engine. We will also explore the specific growth tactics a digital commerce business can undertake to leverage its growth engine for maximum results. If you want to watch the full webinar, which includes both parts, find it here.
Stay in the loop
Subscribe to our newsletter to learn how to build world-class digital experiences and get fit for digital growth.
Stay in the loop
Subscribe to our newsletter to learn how to build world-class digital experiences and get fit for digital growth.

Stay in the loop
Subscribe to our newsletter to learn how to build world-class digital experiences and get fit for digital growth.

Stay in the loop
Subscribe to our newsletter to learn how to build world-class digital experiences and get fit for digital growth.
